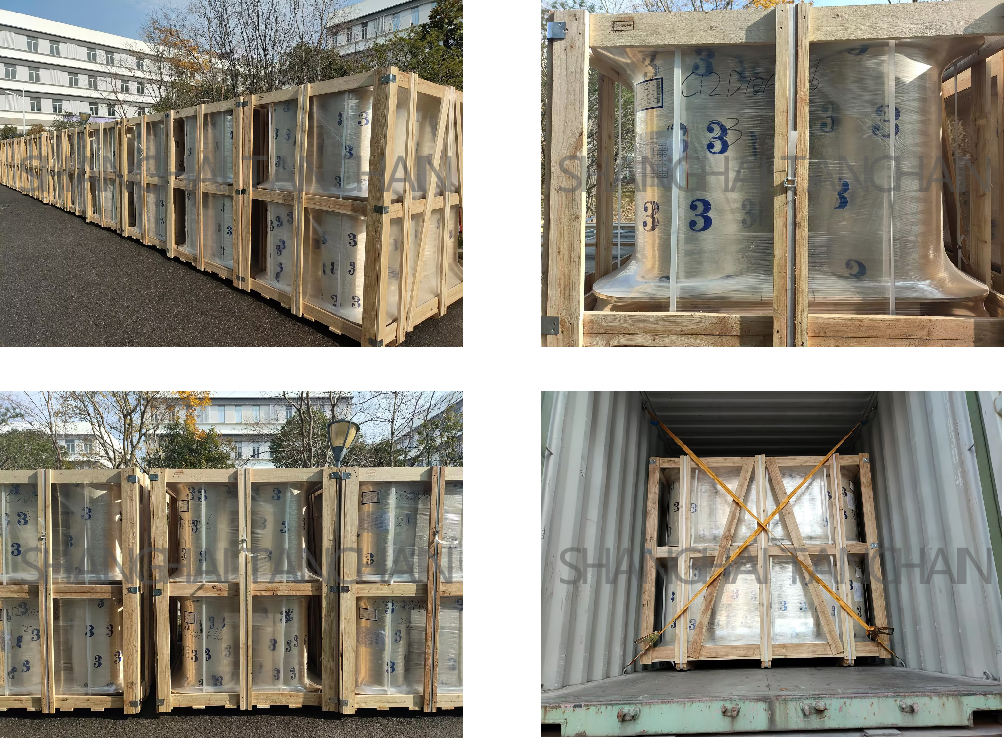
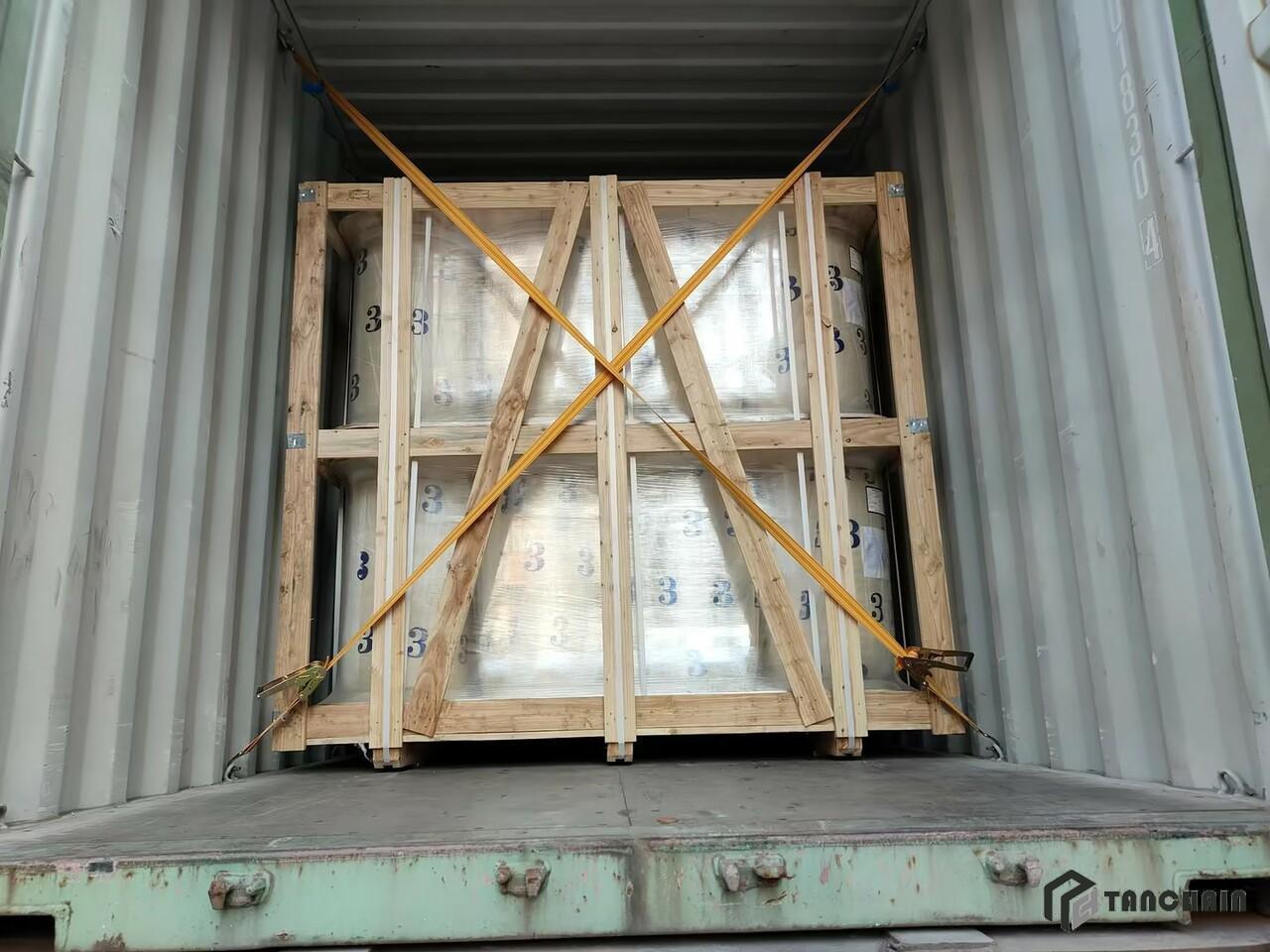
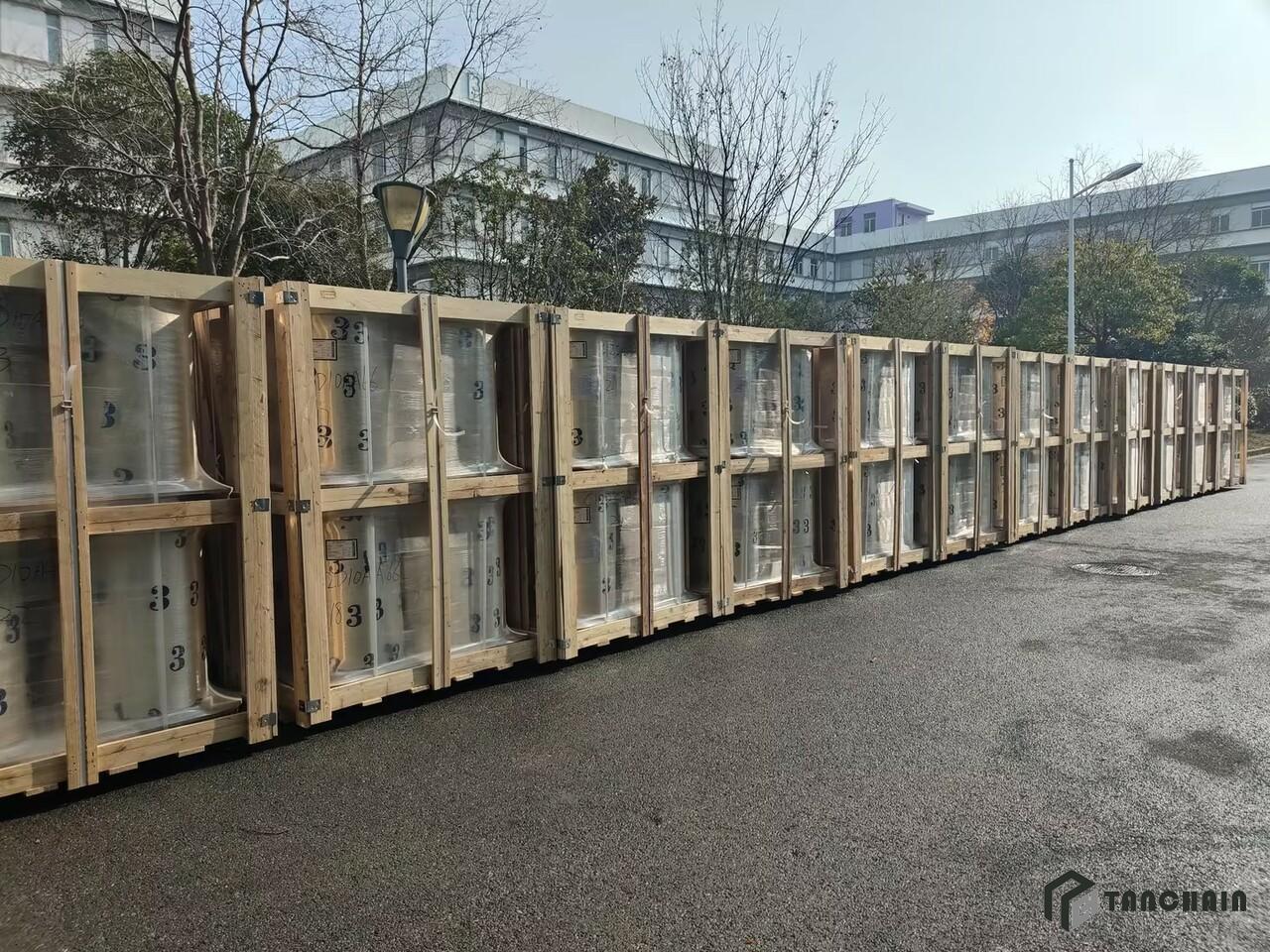
-
-
35K - PAN precursor of carbon fiber
- Code:TC-PAN-35K
- Material:100% Polyacrylonitrile(PAN)
- Weight:35k filaments
- Function:The precusor of carbon fiber
- Color:white
SEND INQUIRY






The main differences between polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber precursor and other carbon fiber precursors are as follows:
Different raw materials
- Polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber precursor: The main raw material is polyacrylonitrile, which is a high molecular polymer formed by the polymerization of acrylonitrile monomer.
- Asphalt-based carbon fiber precursor: Petroleum asphalt or coal asphalt is used as raw material, the raw material cost is low, but the composition is complex and needs to be refined.
- Viscose-based carbon fiber precursor: The main component is cellulose, which is usually derived from viscose fibers obtained by chemical processing of natural fibers such as wood and cotton linters.
Performance characteristics
- Mechanical properties
- Polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber precursor: The carbon fiber produced has high strength and modulus, excellent comprehensive mechanical properties, and can meet the requirements of fields with strict mechanical properties of materials, such as aerospace structural parts.
- Asphalt-based carbon fiber precursor: A higher modulus can be obtained in some directions, but the strength may be slightly lower than that of polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber, but it has advantages in preparing special uses such as high thermal conductivity carbon fiber.
- Viscose-based carbon fiber precursor: The strength and modulus are usually lower than those of polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber, but its toughness is better, and it has certain value in some application scenarios with high flexibility requirements.
- Thermal properties
- Polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber precursor: It has good high temperature resistance and can still maintain high strength and stability at high temperatures. The pre-oxidation and carbonization process enables it to withstand subsequent high temperature treatment.
- Asphalt-based carbon fiber precursor: Its structural transformation mode and thermal stability during high temperature treatment are different from those of polyacrylonitrile-based. The thermal properties vary depending on the asphalt raw materials and treatment process.
- Viscose-based carbon fiber precursor: The thermal stability is relatively poor, and more structural changes and quality losses will occur during the carbonization process, but its thermal properties can be improved through special processes.
Production process
- Polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber precursor: The production process is mature, including polymerization, spinning, pre-oxidation, carbonization and other complex and delicate processes, and high process control requirements are required to ensure the quality of the precursor.
- Asphalt-based carbon fiber precursor: The production process involves the refining of asphalt, direct carbonization or graphitization after spinning, and the process focuses on the pretreatment and spinning of asphalt, as well as the structural control during high temperature carbonization.
- Viscose-based carbon fiber precursor: During production, viscose fibers must first be made into precursors, and then dehydrated, pyrolyzed and carbonized. The process difficulty lies in the pretreatment of viscose fibers and the quality control during the pyrolysis and carbonization process.
Application fields
- Polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber precursor: It is the most widely used and plays a key role in many fields such as aerospace, automotive industry, sporting goods, and building reinforcement, mainly due to its high strength, high modulus and good comprehensive performance.
- Asphalt-based carbon fiber precursor: It is mainly used in some cost-sensitive fields that require special properties such as thermal conductivity, such as building insulation materials, and some industrial insulation or thermal conductive materials.
- Viscose-based carbon fiber precursor: It is relatively less used, and some are used to manufacture special products that require electromagnetic shielding, ablation resistance and other properties, such as aerospace insulation materials.
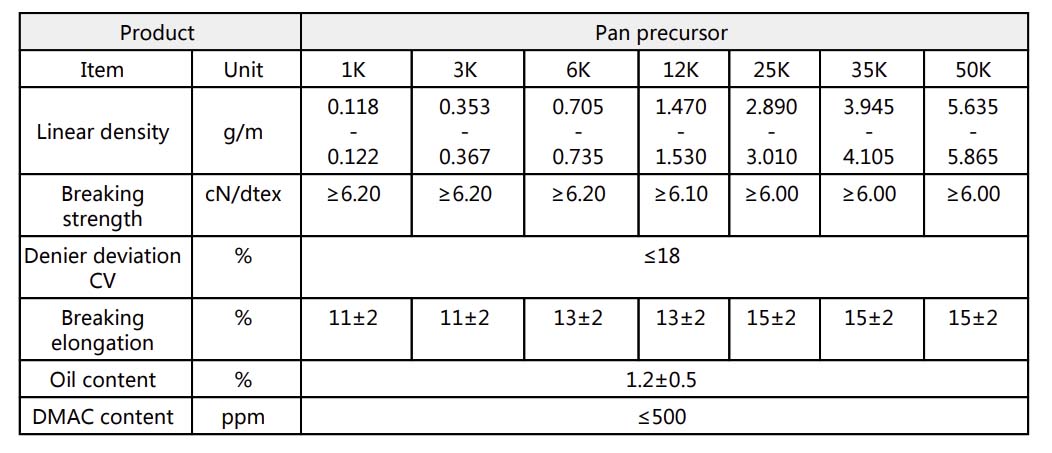
Technical Data Sheet
Tanchain's Production Flow


SHIPPING











